Blog
Difference Between Salary and Wages: A Comprehensive Guide
8 Aug 2024
Wages and salaries are two types of remunerations that should be distinguished when recruiting employees so that the employees are paid fairly, and the company does not violate the employment laws. This distinction not only helps identify the right pay for the employees but also helps control payroll to a very large extent.
In this article, the author will discuss the main aspects of salary and wages, their differences, and the information about the calculation methods, the advantages, the legal aspects, and the permitted deductions.
To get more payroll information, you can turn to PDMC Free Consultation for individual help.
What Are Wages and Salaries?
Definition of Wages
Wages are remunerations given to employees about the amount of work done or the number of goods produced. They may be determined on an hourly rate or based on the number of pieces produced, which makes them very flexible.
Wages are usually used in positions involving physical work or production line work, where the amount of money paid to the employee is proportional to the amount of work they are expected to do.
Definition of Salary
A salary is a predetermined sum of money paid to an employee periodically, for instance, weekly, fortnightly or monthly. This is a characteristic of wages since wages are paid per hour worked or per unit produced, while salaries do not possess this characteristic.
Salaried employees are normally in the professional, administrative, managerial and technical category of employees, focusing on work accomplishment rather than time.

Key Differences Between Salary and Wages
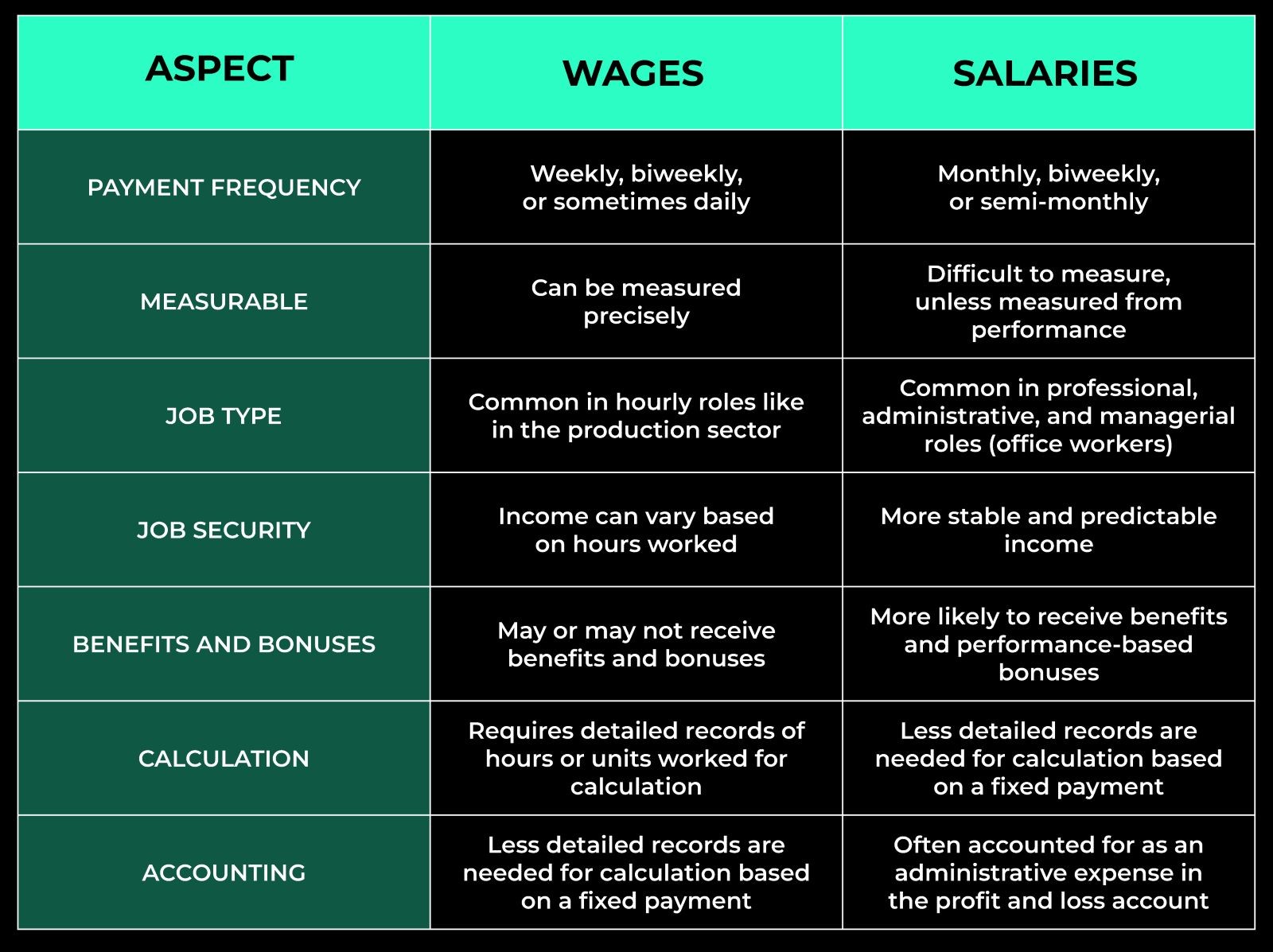
How Wages and Salaries Are Calculated
Calculating Wages
Wages are determined by several factors, including:
Hourly Rate: Multiply the number of hours worked by the hourly wage.
Piece Rate: To get the total cost, multiply the units produced by the rate per unit.
Overtime: Extra pay for extra hours worked in a day, week or month, or additional pay at a higher rate for working at night or on a holiday.
Additional Allowances: Specify other payments, such as bonuses or incentives, that may be offered.
Calculating Salaries
The salaries are determined as a fixed amount paid at regular intervals. This structure includes:
Fixed Payment: A fixed amount of pay regardless of the number of hours the employee has worked.
Additional Benefits: Salary includes bonuses such as medical care, pensions, and vacation pay for the salaried employees.
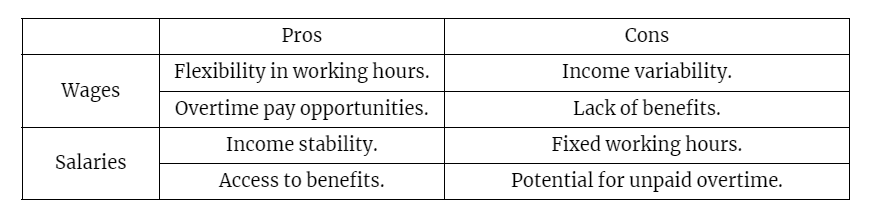
Pros and Cons of Wages and Salaries
Authorised Deductions from Wages and Salaries
Any deductions made from wages and salaries are supposed to be in accordance with the provisions of the law to avoid exploitation of the workers. These deductions are figures the employer is allowed by the law to deduct from employees’ wages in specific circumstances.
To the employer, it is important to understand these deductions because they influence the amount of net pay that the employee receives.
Legal Framework for Deductions
Two primary legal frameworks typically govern deductions:
Shop and Office Workers Act
Section 19 (1): This section posits that payment should be made in cash to the employee, and no deductions are allowed without the employee's consent.
Authorised deductions include:
Advances of Money: The repayment of such loans or advances the employer gives the employee.
Payments to Third Parties: Subtractions for payments made by the employer to any person at the instance of the employee, for example, union fees, insurance or any other fees.
Contributions to Approved Funds: Subtractions for the employees’ provident funds, insurance schemes or other approved frills by the employer.
Limitations: The total deductions at any time must not exceed 60% of the remuneration due.
Wages Board Ordinance
Section 2 (1): This section requires that wages be paid directly to the worker without unauthorised deductions. Authorised deductions include:
Advances of Money: Similar to the Shop and Office Workers Act, this includes repayment of loans provided by the employer.
Third-Party Payments: Subtractions for payments made to third parties on behalf of the employee with their permission.
Approved Contributions: Exemptions that include payments made to approved funds and facilities like retirement funds or health insurance.
Limitations: The amount of permissible deductions also depends on the trade; while some trades allow for deductions of up to 75% of the wages, other trades only allow for deductions of up to 50% of the wages
Common Authorized Deductions
Tax Withholding: Employers must deduct income tax from the wages or salaries of the employees.
Social Security Contributions: Subtracting social security which may be health, pension and other social securities.
Loan Repayments: Subtracting any money lent or given as an advance to an employee by the employer.
Union Dues: Donations to trade unions or any similar organisation.
Insurance Premiums: Exemptions for health insurance sponsored by the employer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between wages and salaries?
Wages are variable and based on hours worked or units produced, while salaries are fixed payments that do not fluctuate with work hours.
Are there legal distinctions between salary and wage?
Yes, different labour laws and regulations apply to wages and salaries, particularly regarding overtime, benefits, and deductions.
Can you provide an example of how to differentiate between salary and wage?
An employee earning wages might be paid $15 per hour for 40 hours a week, while a salaried employee might receive $3,000 monthly, regardless of hours worked.
Is it possible to negotiate a salary or wage offer?
Yes, salary and allowances are negotiable based on job description, experience and market rate. But minimum wages are fixed under the National Minimum Wages Act and some Wages Board Ordinances. Less than that cannot be negotiated.
How do wages work for part-time jobs?
The pay structure for part-time employment is normally based on the number of hours employed multiplied by the hourly pay rate.
Employers, as well as employees, need to know the difference between salary and wages. It helps in determining fair wages, legal requirements and efficient payroll handling. Whether you are an employer or employee or running a business, it is helpful to know these differences to better plan your budget and be content with your job. If you need individual consultation on payroll and compensation, you can contact PDMC Free Consultation.
This complete manual looks at all the important issues to do with wages and salaries and is useful for both the employer and the employee. Thus, by pointing out the difference between salary and wages, we hope that you will be able to make the right choices and avoid common pitfalls related to compensation.




